Understanding Startup Failures: Insights from Venture Capitalists
The journey of a startup is often fraught with challenges, and many do not survive the initial stages. Understanding why startups fail, what venture capitalists (VCs) look for, and the lessons to be learned from these failures can provide valuable insights for aspiring entrepreneurs. In this article, we will delve into these aspects and offer a comprehensive guide to navigating the startup landscape.
The Reality of Startup Failures
Statistics on Startup Failures
- High Failure Rates: Approximately 90% of startups fail, with around 20% failing within the first year and about 50% failing within the first five years.
- Primary Reasons for Failure:
- Lack of Market Need: 42% of startups fail due to a lack of market demand for their product or service.
- Running Out of Cash: 29% of startups fail because they run out of funding.
- Not the Right Team: 23% of startups fail due to issues with the team dynamics or skill gaps.
- Competitive Challenges: 19% of startups fail due to being outcompeted in the market.
What Venture Capitalists Look For
Market Potential
- Large and Growing Market: VCs look for startups operating in large, expanding markets with significant growth potential.
- Scalability: The ability of the business model to scale and achieve substantial growth is crucial.
Strong Team
- Experienced Founders: VCs prefer founders with relevant industry experience and a proven track record.
- Complementary Skills: A well-rounded team with complementary skills across technical, operational, and business functions.
Innovative Solution
- Unique Value Proposition: Startups must offer a product or service that solves a significant problem uniquely and compellingly.
- Competitive Advantage: VCs seek startups with a sustainable competitive edge that sets them apart from competitors.
Traction and Metrics
- Early Traction: Demonstrating initial traction, such as user growth, revenue, or partnerships, is important.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Clear and measurable KPIs that indicate the startup’s growth and potential for success.
Financial Viability
- Sound Financials: A solid financial plan and projections that show a path to profitability.
- Funding Use: A clear plan for how the investment will be used to achieve growth milestones.
Vision and Strategy
- Clear Vision: A compelling vision for the future of the company and the market it serves.
- Strategic Roadmap: A well-thought-out strategy for achieving the company’s long-term goals.
Lessons to Learn from Startup Failures
Understand Market Needs
- Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to ensure there is a genuine need for your product or service.
- Customer Feedback: Continuously gather and act on feedback from potential and existing customers.
Manage Finances Wisely
- Cash Flow Management: Keep a close eye on cash flow and ensure you have enough runway to reach critical milestones.
- Efficient Spending: Be judicious with spending, focusing on areas that drive growth and value.
Build a Strong Team
- Right Talent: Hire individuals who bring the necessary skills and experience to complement the founding team.
- Team Dynamics: Foster a collaborative and supportive team environment.
Adaptability
- Pivot When Necessary: Be willing to pivot your business model or product based on market feedback and changing conditions.
- Continuous Learning: Stay informed about industry trends and be open to learning and adapting.
Focus on Execution
- Execution Excellence: Strong execution is often more important than the idea itself. Focus on delivering results consistently.
- Set Clear Goals: Establish clear, achievable goals and work diligently towards them.
Network and Mentorship
- Leverage Networks: Build and utilize a network of mentors, advisors, and industry contacts.
- Seek Guidance: Don’t hesitate to seek advice and mentorship from experienced entrepreneurs and investors.
Conclusion
Understanding why startups fail and what venture capitalists look for can significantly enhance your chances of success. By focusing on market needs, building a strong team, managing finances wisely, and learning from failures, entrepreneurs can navigate the complex startup landscape more effectively. Embrace the journey with a mindset of continuous learning and adaptability, and leverage the insights of experienced VCs to steer your startup towards success.
For more insights and tips on startup success, visit our blog at Desiree Lovell. Share your thoughts and experiences with startups in the comments below.
Embracing Constructive Failure: Turning Setbacks into Success
Failure is often seen as a negative outcome, but it can be one of the most powerful tools for growth and innovation. Constructive failure involves learning from mistakes, adapting, and emerging stronger. In this article, we’ll explore the concept of constructive failure, how to embrace it, and how it can lead to success. We’ll also include engaging graphics to illustrate key points.
Understanding Constructive Failure
What is Constructive Failure?
Constructive failure is the process of using setbacks as learning opportunities. It involves analyzing what went wrong, understanding why it happened, and applying those lessons to future endeavors.
Key Elements of Constructive Failure
- Learning Mindset: Viewing failure as an opportunity to learn rather than a dead-end.
- Resilience: The ability to bounce back and persist despite setbacks.
- Adaptability: Adjusting strategies and approaches based on lessons learned from failure.
The Benefits of Embracing Failure
Innovation and Creativity
- Encourages Experimentation: Failure often comes from trying new things. Embracing it fosters a culture of innovation and creativity.
- Breakthrough Ideas: Many groundbreaking ideas and inventions have come from initial failures.
Personal Growth
- Builds Resilience: Facing and overcoming failure builds mental toughness and resilience.
- Improves Problem-Solving Skills: Analyzing failures helps develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Organizational Improvement
- Identifies Weaknesses: Failure reveals weaknesses in processes and systems, providing an opportunity to address them.
- Enhances Team Collaboration: Working through failures together can strengthen team dynamics and communication.
How to Embrace Constructive Failure
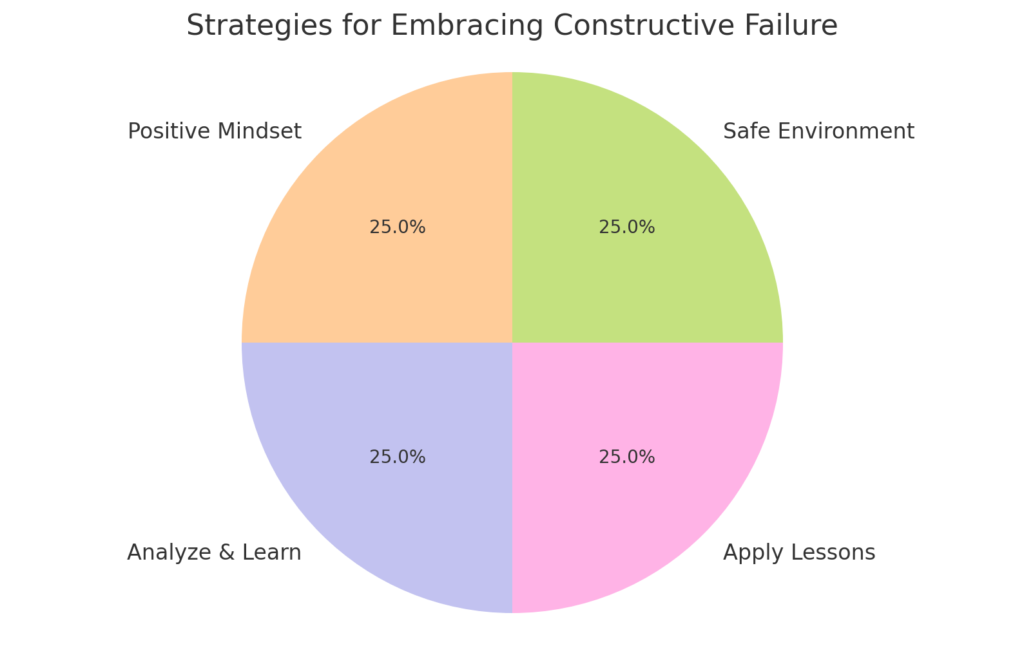
1. Foster a Positive Mindset
- Reframe Failure: View failure as a stepping stone to success.
- Celebrate Effort: Recognize and celebrate the effort and learning involved, not just the outcome.
2. Analyze and Learn
- Conduct Post-Mortems: After a project or task, analyze what went wrong and what can be improved.
- Gather Feedback: Collect feedback from team members and stakeholders to gain different perspectives.
3. Apply Lessons Learned
- Adjust Strategies: Implement changes based on the insights gained from failures.
- Share Knowledge: Encourage a culture of knowledge-sharing where lessons learned from failures are communicated across the organization.
4. Encourage a Safe Environment
- Promote Psychological Safety: Create an environment where team members feel safe to take risks and fail without fear of blame.
- Support Risk-Taking: Encourage calculated risk-taking and experimentation.
Embracing constructive failure is crucial for personal and organizational growth. By fostering a positive mindset, analyzing and learning from setbacks, and creating a supportive environment, you can turn failures into valuable opportunities for success. Remember, every failure brings you one step closer to your goals.
For more insights and tips on personal and professional growth, visit our blog at Desiree Lovell. Share your thoughts and experiences with constructive failure in the comments below.